Traffic Decisions
DESCRIPTION:
Driving on the road in today’s traffic presents a variety of challenges for any driver. The transportation system of roads is very congested and although various government agencies work to create better driving conditions and traffic flow the problems always seem to be getting worse. Keeping up with the growth of traffic on the road system is a never-ending task that continuously has the unfortunate predicament of being behind in applications and improvements. With states and the federal government attempting to keep the roads in good repair and struggling to make improvements constantly, it is inevitable that construction will affect the driver’s environment at some point.
Construction often causes lane changes, changes in road surface, detours, adjustment of permanent traffic controls such as traffic lights and stop signs and anything else that can affect the driver. Construction is only one of the many hazards facing anyone venturing out on the road in an automobile. Accidents often happen and when they do, can affect many people on the same roadway and often impacts surrounding byways. An accident can stack up traffic for miles. Police and other emergency workers have to manage detours and attempt to change the traffic pattern to accommodate blocked roadways and lanes. In many cases, the entire route is shut down in both directions due to the severity of the accident. When these types of incidents happen the police, and other safety personnel must determine how to route traffic to avoid long backups and time spent sitting in traffic by drivers. Communicating the instructions to drivers just trying to get past and continuing their particular travel plans is difficult. Permanent traffic control devices such as traffic lights, stop signs, etc. can affect the flow of traffic as much as any scenario. Problems arise when the traffic lights malfunction or require changes because of construction or other situations. Familiar stop signs can become a problem when construction or accidents cause changes in their location. An intersection that the day before had no stop sign can suddenly become a 4-way stop due to construction or other causes catching the drivers unaware.
The very mobile society in the United States depends on the automobile and truck to get people to places they need to be. Accidental disruptions and intentional changes in routes and roadways can create traffic situations that could be avoided or improved by increasing the communication to drivers of their changing road conditions. Knowledge of accidents, construction, or any change in road conditions before the situation is encountered can help drivers cope with traffic and allow them to adjust their driving or routes to create a safer and improved driving experience.
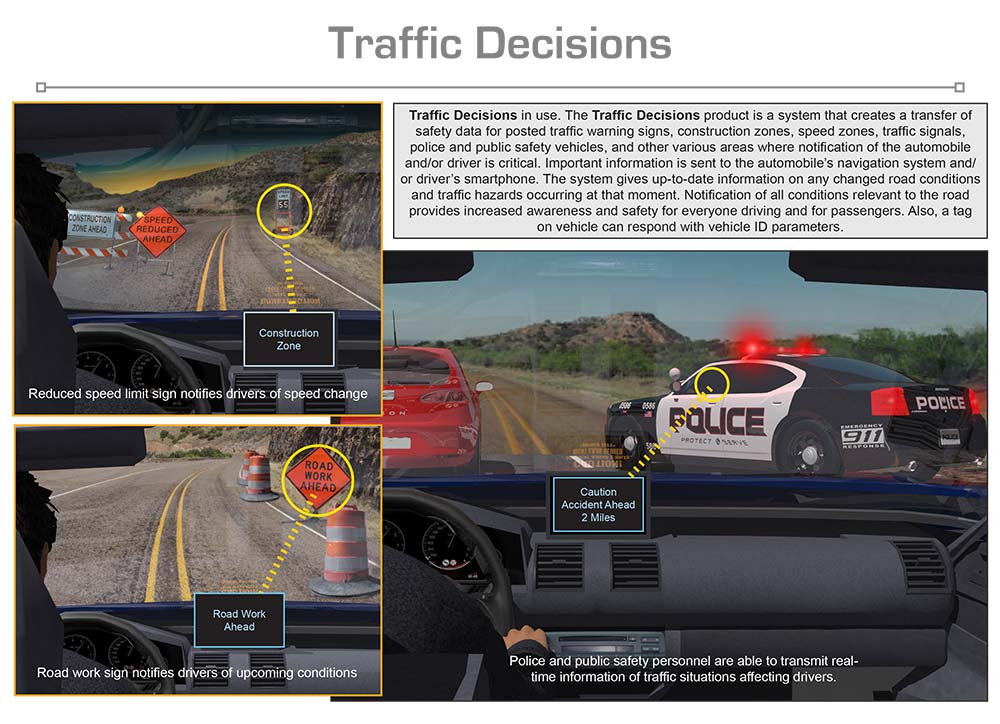
The Traffic Decisions is a unique and innovative product designed to enhance the automobile and truck driver’s interaction with their driving environment. The Traffic Decisions allows traffic relevant data to communicate to the driver’s navigation device or smart-phone for up-to-date situational awareness. Temporary traffic signs such as speed reductions, constructions zones, relocated stop signs, etc. are fitted with a programmable module that is transmitted to the driver’s vehicle. The module will transmit relevant data that particular sign is trying to communicate directly to all vehicles traveling that route. Sudden changes that require lane closures or re-routing of traffic can be communicated to drivers affected by police officers or public safety personnel. The messages can be instantly updated to reflect changing conditions. Traffic lights and permanent traffic controls signs (stop signs, yields, etc.) are fitted with a device that transmits their status and location (or changes in case of damage or relocation due to unforeseen events.) The receiver module can be either a built-in unit provided by the manufacturer or an after- market model that can be affixed to the forward-facing area of the automobile and synced to the navigation system or a smart-phone. The Traffic Decisions is a product that will increase safety on the road by creating communications between the road signs, traffic control devices, law enforcement, etc. and the vehicle driver.
SPECIFIC, UNIQUE FUNCTIONS OF INVENTION:
- Transmits data to the navigation system or smart-phone
- Makes driver directly aware of road conditions ahead
- Police can transmit accident information and instructions to drivers
- Works will all models of cars and trucks
- Show status of traffic lights and locations
- Communicates to drivers when approaching a stop sign or yield
- Police or emergency vehicles can program a tag to provide alerts
- Devices can be programmed quickly
- Data can be made available to autonomous vehicles
- Reinforces visual traffic signs for better communication of situation
- Good for temporary or permanent traffic control devices
- Works with any style of smart-phone
- Improves overall safety and awareness of drivers
- Vehicles can also have a permanent tag indicating ID parameters
(footprint of car, truck with trailer, length, oversize)
PRODUCT COMPONENT CLARIFICATION:
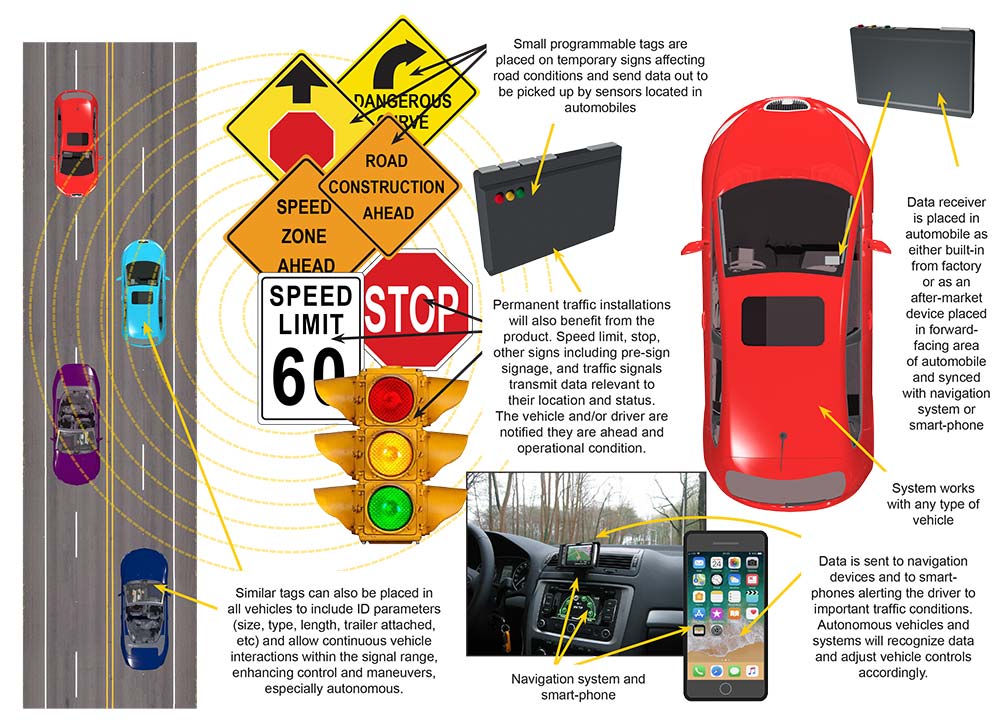
The “Traffic Decisions” is an innovative vehicle safety product that has been designed to allow interrogation and transfer of current data from roadside traffic, maintenance, and other signs to the vehicle’s navigation or smartphone mapping system. (Beyond the example used for this presentation, the system can also be used as tags in all vehicles to allow various vehicle interactions and decisions enhancing and controlling traffic flow). The system consists of an RFID reader mounted up on the vehicle’s windshield that interrogates any and all active RFID tags placed on signs, warning, or other roadside devices. The tags are programmed with the current problem, like ‘right lane closed ahead in 0.3 mile’ and can be placed in the temporary signage erected on the shoulder. The vehicle reads the tag and relays the information to the navigation or smartphone mapping system in the vehicle, alerting the driver to the problem well before it is encountered. The reader is battery powered and recharged overnight using the vehicle’s power.
Currently, the driver is typically unaware of newly developing traffic problems, for example, the one lane of the road is closed due to an accident, the road is being worked on and lane changes are occurring, the road’s speed limit is changing to 35 mph, etc. All of these real-time problems occur, the traffic slows suddenly due to back pressure, additional accidents occur, damaging vehicles and causing injury or death to the driver and occupants.
The “Traffic Decisions” resolves almost all these problems by providing real-time warnings to drivers passing by, which are announced by the navigation or smartphone mapping functions, both audibly and visually. These warnings allow the driver to slow down, take alternate routing, turn off, switch lanes, or generally just be aware that something is occurring ahead. The active RFID tags are programmable using the supplied application and Bluetooth link. This allows any authorized user to program a short message into a tag and place it alongside the roadway, describing the problem. The uses are varied, the messages, while short, can convey a significant amount of data, and the tags are easy to program. The tags battery life is from 4 to 5 years under normal conditions so the tags can be programmed and placed almost anywhere for extended use.
- While this document describes the system for use on normal road changes, the product can be used in hundreds of other applications. All that is required is a reader in the vehicle and programmed tags to instruct the users as to what action they should take. This could be from any moving vehicle with fluid end use requirements like trams taking visitors to entrance gates whose locations change as the buildup of entrants change, mining vehicles with changing underground roadways, military convoys with multiple bivouac locations, to large event campgrounds, etc.
- The tags can be placed on permanent alert signage not only to indicate change of information different than presented in navigation applications, but also for normal information alerts such as speed limit, stop, and other signs or signals.
- The system is described as an aftermarket product herein. The product could easily be supplied as part of the original equipment manufactured on the vehicle and unobtrusively integrated into the common telematics package supplied on the vehicle.
The RFID reader: The reader is protected with an injection molded polycarbonate/ABS plastic housing. The housing is molded is 2 sections and has retention studs into which the stainless steel fasteners are driven to hold the front and rear sections together. This plastic is very durable, is highly resistant to household chemicals, is highly resistant to drop shocks, and is typically used in this type of application. The housings can be supplied in almost any vibrant color, so a distinctive color may be chosen to enhance the product recognition factor, which can dramatically improve the market adoption of the product. The front section of the housing has all the components mounted within to facilitate assembly. The internal electronics are, but not limited to, the following subcomponents.
- The controlling computer: Dual core, 2.0 GHz ARM based computer chipset. This is from a generation back cellular phone inventory to reduce programming and device cost. The product is supplied with 16 GB of memory and 1 GB of RAM.
- LEDs: These low current LED devices are lighted using a remote LED driver controlled by the computer. They indicate status and current conditions of the device to aid in quickly determining the condition of the system. They work in conjunction with the touch screen display. They consist of a red, green, and amber LED.
- Red: means the system needs to be charged.
- Green: means the system is on and is within operating parameters.
- Amber: means the system needs power soon.
- Switch: The switch is a sealed tactile membrane switch, which are used to operate the microcomputer.
- The 2.45 GHz transceiver: This RF transceiver is optimized to randomly scan between 2.435 and 2.465 GHz to excite any active RFID tags within the 400’ free air range. The system is also bi-channel to accept any RFID tag data, decode it, and pass it along to the computer for transfer via the Bluetooth link to the vehicle’s navigation or the smartphone being used in the mapping mode. The data is then audibly and visually presented to the driver. The antenna can be etched and plated in the normal PCB construction or it can be a wound wire unit attached to the PCB in construction.
- The WiFi link: 802.11 a/b/g/n, dual band chip set.
- GPS chipset: This chipset uses GPS/GNSS solutions to provide meter-level accuracy
positioning. The optimized signal and satellite acquisition provides reliable positioning
under attenuated indoor and difficult urban canyon environments. - The Bluetooth link: 5.0, A2DP, and LE (long range) capable chip set. This unit can send and receive up to 300’ in free air. Somewhat less within building confines but
more than sufficient for this application. - Li-Ion battery: This very high current density battery employs the latest in Li-Ion
technology. It is packaged to fit in the housing. When fully charged, the battery will support normal operation over approximately 24 hours after loss of charging power.
- LEDs: These low current LED devices are lighted using a remote LED driver controlled by the computer. They indicate status and current conditions of the device to aid in quickly determining the condition of the system. They work in conjunction with the touch screen display. They consist of a red, green, and amber LED.
The active RFID tag: These module’s housings are injection molded using ABS polycarbonate plastic. This plastic is very durable, is highly resistant to household chemicals, is highly resistant to drop shocks, and is typically used in this type of application. The housings can be supplied in almost any vibrant color, so a distinctive color may be chosen to enhance the product recognition factor, which can dramatically improve the market adoption of the product or the product can be observed by an authority from some distance. The housing sections are adhesively bonded together to make the package waterproof. They can be placed on any ferrous sign or flat surface using the magnets, or placed in a sewn pocket in a temporary sign, or just placed near the roadway at a place where they will not be run over. They could even be hung in a temporary pocket hanging from side window of the police, fire, or other vehicle at the side of the road. The internal electronics are, but not limited to, the following subcomponents.
- The computer: This is a very low power requirement, 8-bit RISC, solitary chip microcontroller operating at 16 MHz. It has onboard chip flash memory, 256 KB flash and 32 KB, which can be increased through the use of external sources if more memory is required. The chip also a few pins available that are capable of being paralleled together so it can drive a low power LED indicator directly, if required.
- The 2.45 GHz transceiver chip set: This RF transceiver is optimized to reply to any reader signal between 2.435 and 2.465 GHz. The signal excites it to reply with its serial number and pre-programmed data. The antenna can be etched and plated in the normal PCB construction or it can be a wound wire unit attached to the PCB in construction.
- The Bluetooth link: 5.0, A2DP, and LE (long range) capable chip set. This unit can send and receive up to 300’ in free air. Somewhat less within building confines but more than sufficient for this application.
- Batteries: These are commercially available, lithium iron sulfate primary AA batteries. They have a very wide temperature capability (-55°C to +125°C) so they will operate in any outdoor environment. In normal usage they will last up to 5 years of normal use with a 10-year storage capability. The tag reports low battery conditions so the authority’s reader/programmer can alert the operator setting up the tag data that they should take the tag out of service and return it to the manufacturer for refurbishment.
The printed circuit boards (PCBs): The PCBs for all devices are fabricated to the final assembler’s requirements in a world class contract electronic assembler facility. The standard thickness, double sided FR4 circuit board material is populated with surface mounted components where possible. Any through-hole devices are inserted after the surface mounted assembly, soldering, and cleaning. Both circuit boards are designed to have all the components oriented so they can be mounted with the LED illuminators projecting out of the lenses mounted in the housings. After assembly, the PCBs are protected with a moisture adsorption preventive conformal coating.
The programmer application: This application is a one-time written program that can be used on a tablet, laptop, or smartphone that is equipped with Bluetooth. The tag is paired to the programming device through the app and the data message can be typed in using the programming device’s keyboard. This message, although it must be just a few characters, can convey considerable data. This can be as simple as ‘Road Work Ahead’, ‘Left Lane Closed in 0.5 Miles’ or, ‘Vehicle Wreck ahead in 1 Mile’, ‘Turn left in 400 feet’, etc. The programming system is designed to be easy to use so any first responder or designated state/local technician can write to a tag and place it to help warn the reader equipped vehicles of a condition change ahead. The tags can also be placed on a permanent road sign and be left there until the battery runs down, whereupon a replacement tag can be swapped in.
The Traffic Decisions product is designed to be aesthetic and effective in the application. The relative ease of manufacture and the moderately inexpensive components provide good marketability for the manufacturer. The user benefits from improved road condition awareness and resultant safety, which should provide considerable market interest in the product.
The invention is illustrated in the following drawings of the essential points as explained to us in the documentation.
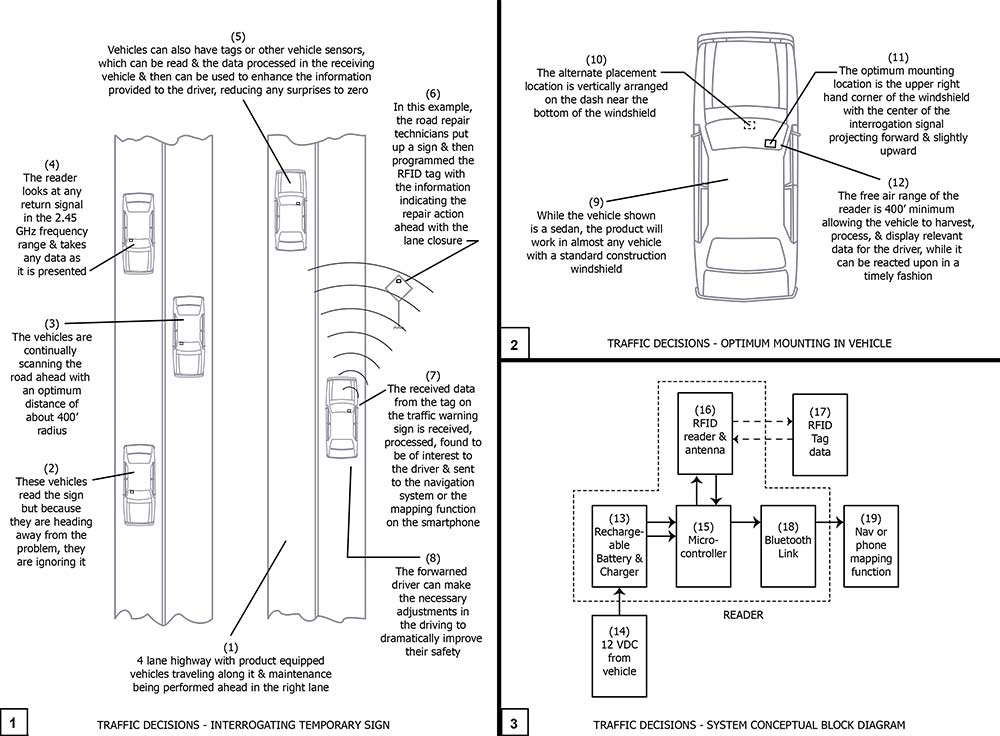
Drawing 1, Block 1: Traffic Decisions – Interrogating Temporary Sign
(1) 4 lane highway with product equipped vehicles traveling along it and maintenance being performed ahead in the right lane. The temporary signs are made of sewn nylon on weighted base and are altered to have a small pocket into which the programmable RFID tag can be dropped.
(2) These vehicles read the sign but because they are heading away from the problem, they are ignoring it.
(3) The vehicles are continually scanning the road ahead with an optimum distance of about 400’ radius. As the technology matures, greater and greater ranges will be developed, improving the read and react times.
(4) The reader looks at any return signal in the 2.45 GHz frequency range and takes any data as it is presented.
(5) Vehicles can also have tags or other vehicle sensors, which can be read and the data processed in the receiving vehicle and then be used to enhance the information provided to the driver, reducing any surprises to zero.
(6) In this example, the road repair technicians put up the sign and then program the RFID tag with the information indicating the repair action ahead with the lane closure.
(7) The received data form the tag on the traffic warning sign is received, processed, found to be of interest to the driver, and sent to the navigation system or the mapping function on the smartphone. Any navigation system in use with a Bluetooth link can be paired with the reader to receive the real-time data received from the programmed RFID roadside tags.
(8) The forewarned driver can make the necessary adjustments in the driving to dramatically improve their safety.
Drawing 1, Block 2: Traffic Decisions – Optimum Mounting In Vehicles
(9) While the vehicle shown is a sedan, the product will work in almost any vehicle with a standard construction windshield.
(10) The alternative placement location is vertically arranged on the dash near the bottom of the windshield.
(11) The optimum mounting location is the upper right hand corner of the windshield with the center of the interrogation signal projecting forward and slightly upward.
(12) The free air range of the reader is 400’ minimum allowing the vehicle to harvest, process, and display relevant data for the driver, while it can be reacted upon in a timely fashion.
Drawing 1, Block 3: Traffic Decisions – System Conceptual Block Diagram
(13) Rechargeable battery and charger
(14) 12 VDC from the vehicle
(15) Microcontroller
(16) RFID reader and antenna
(17) RFID tag data
(18) Bluetooth link
(19) Nav or phone mapping function
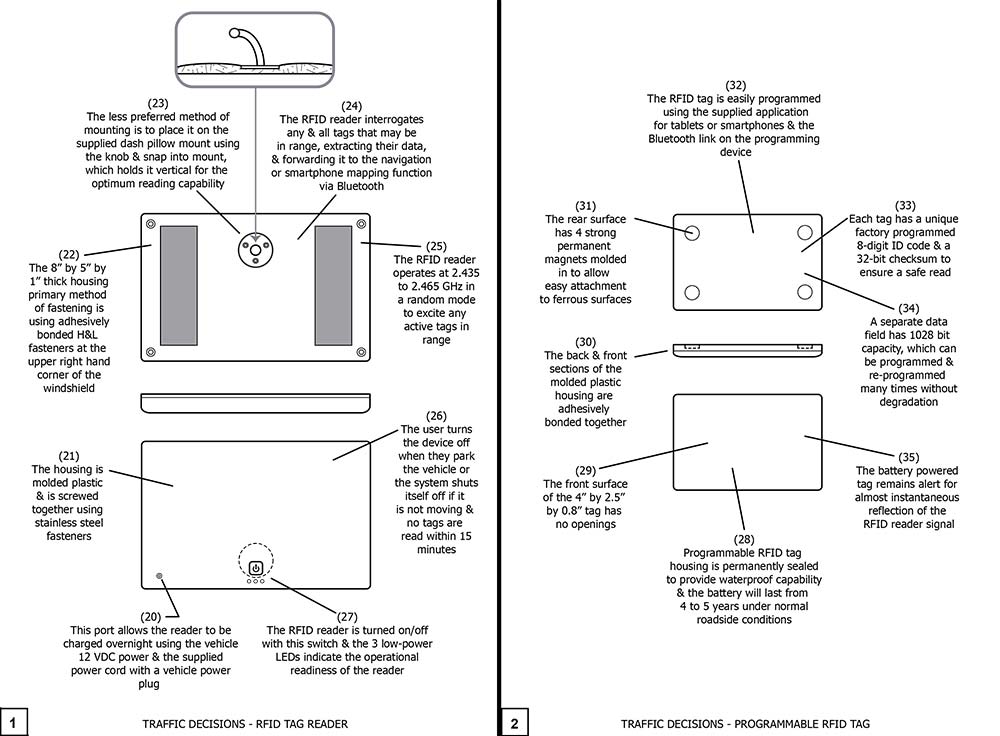
Drawing 2, Block 1: Traffic Decisions – RFID Tag Reader
(20) The port allows the reader to be recharged overnight using the vehicle 12 VDC power and the supplied power cord with a power plug.
(21) The housing is molded plastic and is screwed together using stainless steel fasteners.
(22) The 8” by 5” by 1” thick housing primary method of fastening is using adhesively bonded H&L fasteners at the upper right corner of the windshield. These fasteners adhesive operates over a very wide temperature range and is not significantly affected by ultraviolet exposure over time. The two, 1” wide by 4” long H&L fasteners are capable of holding up over 200 pounds, easily securing the product to the windshield.
(23) The less preferred method of mounting is to place the it on the supplied dash pillow mount using the knob and snap into mount, which holds it vertical for the optimum reading capability.
(24) The RFID reader interrogates any and all tags that may be within range, extracting their data, and forwarding it to the navigation or smartphone mapping function via Bluetooth.
(25) The RIFD reader operates at 2.435 to 2.465 GHz in a random mode to excite any active tags in range.
(26) The user turns the device off when they park or the system shuts itself off if it is not moving and no tags are read within 15 minutes. When turned off, there are no LEDs on and last message sent to the navigation or phone system is ‘Traffic Decisions system is off’.
(27) The RFID receiver is turned on/off with this switch and the 3 low power LEDs indicate the operation readiness of the reader.
Drawing 2, Block 2: Traffic Decisions – Programmable RFID Tag
(28) Programmable RFID tag housing is permanently sealed to provide waterproof capability and the battery will last from 4 to 5 years under normal conditions.
(29) The front surface of the 4” by 2.5” by 0.85” thick tag has no opening.
(30) The back and front sections of the molded plastic housing are adhesively bonded together.
(31) The rear surface has 4 strong permanent magnets molded in to allow easy attachment t ferrous surfaces. The unit can be placed in a pocket sewn into the sign, can be strapped to the surface using a nylon strap, or taped using non-metallic strapping tape.
(32) The RFID tag is easily programmed using the supplied application for tablets or smartphones and the Bluetooth link on the programming device.
(33) Each tag has a unique factory programmed 8-digit ID code and a 32-bit checksum to insure a safe read.
(34) A separate data field has a 1028-bit capacity, which can be programmed and re- programmed many times without degradation.
(35) The battery powered tag remains alert for almost instantaneous reflection of the RFID reader signal.
Although a single embodiment of the invention has been illustrated in the accompanying drawings and described in the above detailed description, it will be understood that the invention is not limited to the embodiment developed herein, but is capable of numerous rearrangements, modifications, substitutions of parts and elements without departing from the spirit and scope of the invention.
This document has been prepared for the manufacturer’s elucidation. The manufacturer’s decision makers should consider this product for licensing (providing intellectual property protection for their sales of the product in return for a royalty payment for a period of years) or an outright purchase of the patent for a negotiated fee. The inventor and his team are standing by to consider offers for licensing or outright purchase of the patent.